
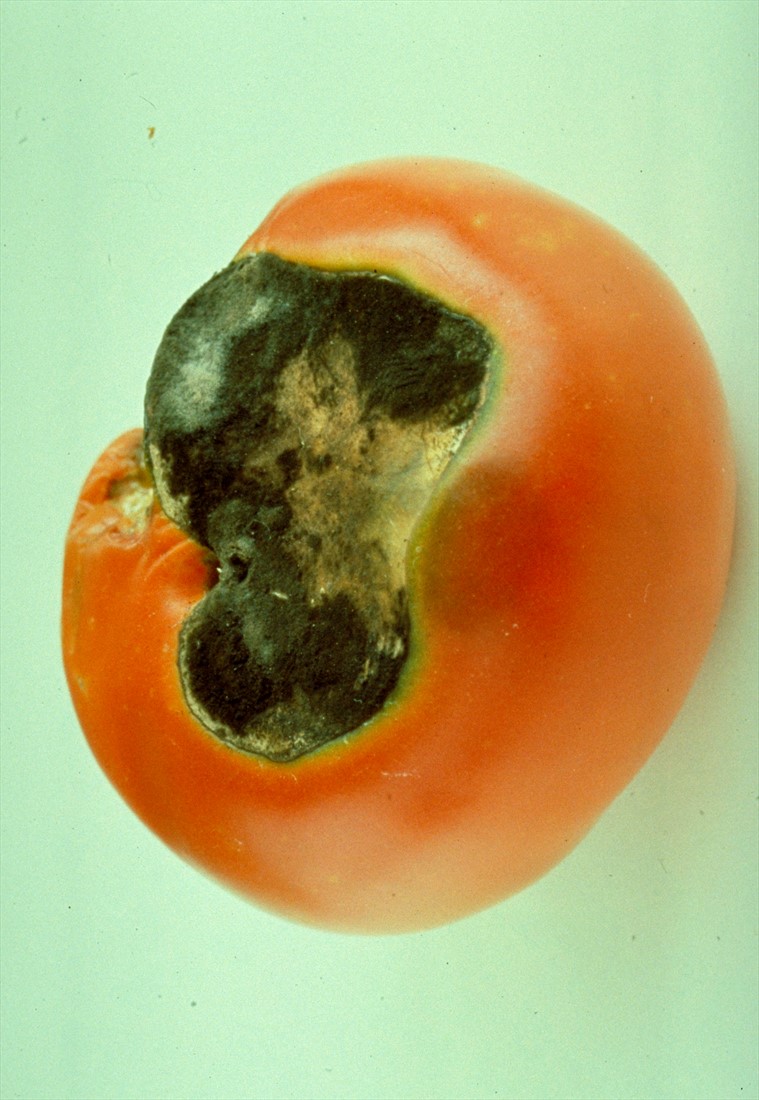
Moisture creates ideal circumstances for spores to grow. Tomato Blight Cultural Prevention Watering The illness will spread if tomatoes are stored in warm, humid conditions. Late blight can swiftly damage leaves and spread down the petiole into the stem, eventually killing the plant. The dark, granular rot with vague boundaries may be seen extending into the pulp when the fruit is sliced.
EARLY TOMATO BLIGHT CURE SKIN
The illness causes the tomato skin to develop a dark purple tint. It is famous for creating the Irish Potato Famine of the 1840s, which killed a million people and resulted in the huge migration of over a million and a half Irish nationals. Late blight is the most serious disease that affects potatoes and tomatoes. Stem lesions are dark brown in colour and have well-defined edges. Infested tomatoes emit a nasty, decaying stench. A white, fluffy growth surrounds the rotting region on the underside of the leaves during wet weather. The dots expand into big black and purple patches as they mature. These lesions do not have leaf veins and can develop across them. The illness is distinguished by tiny, necrotic, water-soaked light to dark green patches that are frequently encircled by yellowish rings. Late blight affects tomato plants and also potatoes. Phytophthora infestans, which means “plant destroyer” in Latin, is late blight. Black, blistering blotches appear on infected fruits. The dark brown lesions on the leaves will swiftly get larger in warm and humid conditions, causing chlorosis and considerable defoliation, leading to sunscald. The blight spreads throughout the fruit via insect attachment points or wounds, contaminating the entire fruit. For tomato farmers, the destruction caused by the blight can be devastating making for a long growing season.Įarly blight can cause collar rot, which renders stems dark, dry, and depressed and causes seedling mortality. Early blight, as the name suggests, usually strikes during early tomato season, while the late blight strikes in the mid-to-late season.Īlthough these diseases are made up of different microorganisms, the result is the same. Blight on tomato plants causes them to die back near the base of the plant, resulting in dead leaves at ground level, which can be seen easily. Tomatoes are susceptible to stress due to diseases such as blight caused by fungi, especially when growing under warm conditions during the summer months. In general, tomatoes prefer acidic soil with low levels of nitrogen (N) fertilizer applied during vegetative growth stages however, some varieties may prefer higher levels than others (Gralinski et al. Tomato plants need warm soil temperatures between 20☌ and 30☌ (68☏ and 86☏) with at least 6 hours of sunlight a day for optimal growth rates throughout their lifecycle (Flannigan & Sloane 1998). When growing tomatoes, it is important to ensure that they are planted at the right time of year for their area of origin and climate conditions (i.e., early spring or late summer). It quickly spread throughout Europe and was later introduced to North America by Spanish colonists. It was first cultivated in Mexico and Central America before spreading to Spain during the 16th century. The species is believed to have originated in South America.


It is grown in a variety of ways, including as an annual or biennial plant, as a vine or as a perennial herb.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/blight-on-tomato--empire-hybrid----vegetable---septmeber--winter--128128344-5b22a3498023b9003682c8ce.jpg)
The tomato is a popular fruit and vegetable crop in many parts of the world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
